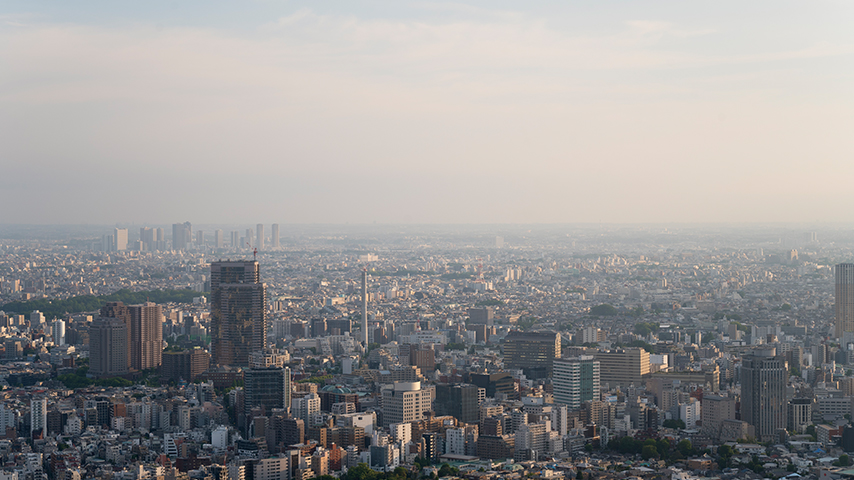
Understanding Tier I, Tier II, and Tier III Cities in India’s Diverse Landscape
First, let us understand what Tier I, Tier II, and Tier III cities are, as India is a vast and diverse country with many cities that offer different opportunities and challenges for any kind of business growth, and the same is true for real estate development in that area.
According to the Central Government, cities are widely divided on the basis of their population.
Tier I cities like Mumbai, Delhi, Pune, Chennai, Bangalore, etc. have populations of 100,000 and above. Whereas Tier II cities like Nagpur, Vizag, Lucknow, Surat, Jaipur, Indore, Mangalore, etc. have populations of 50,000 to 100,000, and lastly, Tier III cities like Gandhinagar, Roorkee, Vijayawada, Udaipur, and Nashik have populations of 20,000 to 49,999.
Tier 2 cities offer many advantages for real estate investors
-
Economic Growth
Tier 2 cities are witnessing robust economic growth, fuelled by a shift towards decentralisation and government initiatives to promote regional development.
-
Infrastructure Development
Many Tier 2 cities are experiencing significant infrastructure development, including the expansion of transportation networks, the establishment of industrial parks, and the improvement of social amenities. This enhances connectivity and liability, making these cities attractive for real estate investments.
-
Lower Costs
Compared to Tier 1 cities, Tier 2 cities offer lower land and property prices, making them more affordable for investors. This affordability, coupled with the potential for high returns, presents a lucrative opportunity for both residential and commercial real estate investments.
-
Growing Middle-Class Population
Tier 2 cities are witnessing a rise in the middle-class population, leading to increased demand for housing, retail, and entertainment options.
-
Diversification
Investing in Tier 2 cities allows investors to diversify their real estate portfolios beyond the saturated Tier 1 markets.
-
Government Support
The government’s focus on urban development and smart city initiatives has directed attention towards Tier 2 cities.
-
High Quality of Life
Tier 2 cities often offer a better quality of life with less congestion, a cleaner environment, and access to amenities. These factors attract individuals and businesses looking for a balance between urban comforts and a relaxed lifestyle.
Real Estate development in Tier 3 cities in India
With already developed infrastructure and transportation, Tier 1 cities already have a strong and established real estate market, while Tier 2 cities are experiencing rapid growth.
Similarly, Tier 3 cities also show great potential for development. There is a significant difference between Tier 3 cities and Tier 1 cities in terms of real estate prices. Real estate prices in Tier 3 areas are lower than in large cities due to a lower level of development. The result is a decrease in the price of assets, especially land and construction materials. Moreover, these cities are undergoing substantial development; hence, investors see this as a good opportunity for investment. In Tier 3 cities, residential and commercial property costs are comparatively lower than in Tier 1 cities.
Future prospects:
As the focus shifts beyond metropolitan regions, especially after COVID, where there was a reverse migration from metro to smaller towns and cities, these cities are now expecting to witness sustained economic growth, infrastructure development, and increased demand for real estate. Factors such as government initiatives like “Smart City” projects, improving connectivity, favourable investment policies, and the decentralisation of industries contribute to their overall growth potential.
Conclusion:
Both Tier II and Tier III cities offer a combination of affordability, quality, growth, and potential that is hard to find in Tier 1 cities. However, one must carefully assess the risks and challenges associated with investing in these cities and conduct thorough research before making investment decisions.
Check out Ideas for a Sustainable Commercial Projects
Know more about Real Estate Business Management Program